2023 Spring 《服务端开发》课程全部录屏地址:2023 Spring-服务端开发 。视频来源正当,仅供学习。
建立开发环境
依赖
spring-boot-devtools spring-boot-starter-web
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
参考《Spring 实战(第 5 版)》1.1.2 节、1.3.5 节。
代码变更后应用会自动重启(需要借助 IDE 的自动编译)
当面向浏览器的资源(如模板、JavaScript、样式表)等发生变化时,会自动刷新浏览器
应用会暴露 LiveReload 端口,日志如:LiveReload server is running on port 35729
需要安装 VSCode 插件 LiveReload (IntelliJ IDEA 要做的配置见下页 ppt)
需要安装浏览器插件:LiveReload,并打开
自动禁用(页面渲染的)模板缓存
如果使用 H2 数据库,则内置了 H2 控制台。访问:http://localhost:8080/h2-consle
强调:该工具只在运行期使用 ,所以依赖包中它的依赖范围是 Runtime,与编译器无关,不会有编译优化。
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-devtools</artifactId > <scope > runtime</scope > </dependency >
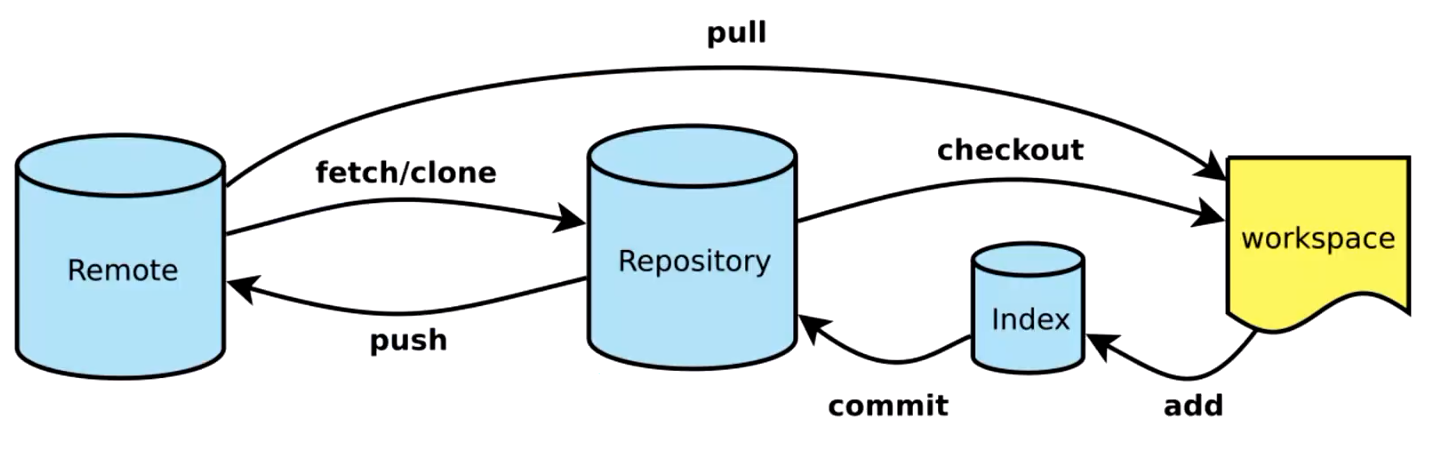
源代码仓库管理
也称为版本控制(version control)系统,常用工具有:GitLab、SVN(Subversion)、Bitbucket 等;
需纳入版本控制的有:功能代码、测试代码、测试脚本、构建脚本、部署脚本、配置文件等;
从暂存区(index)提交到本地仓库使用的命令是 git commit。
依赖注入
依赖注入(Dependency Injection),又叫控制反转(IoC)
Spring 的两个核心技术:
DI (Dependency Injection):保留抽象接口,让组件(Component)依赖于抽象接口,当组件要与其他实际的对象发生依赖关系时,由抽象接口来注入依赖的实际对象
AOP (Aspect Oriented Programming):通过预编译方式和运行期间动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。利用 AOP 可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发效率
Spring 的核心是提供了一个容器(container)
Spring 配置方案【可能考简答】
参考《Spring 实战(第 5 版)》1.1 节。
XML 配置
参加代码 section2-4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 <bean id="compactDisc" "soundsystem.BlankDisc" "Sgt. Pepper's Lonely Hearts Club Band" "The Beatles" >'s Lonely Hearts Club Band</value> <value>With a Little Help from My Friends</value> <value>Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds</value> <value>Getting Better</value> <value>Fixing a Hole</value> <!-- ...other tracks omitted for brevity... --> </list> </constructor-arg> </bean>
JavaConfig
参加代码 section2-2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 @Configuration public class CDPlayerConfig {@Bean public CompactDisc compactDisc () {return new SgtPeppers ();@Bean public CDPlayer cdPlayer (CompactDisc cd) {return new CDPlayer (cd);
自动化配置
参加代码 section2-1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Component public class CDPlayer implements MediaPlayer {private CompactDisc cd;@Autowired public CDPlayer (CompactDisc cd) {this .cd = cd;public void play () {
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public class MyAnnotationApp {public static void main (String[] args) {ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext (CDPlayerConfig.class);MediaPlayer player = ctx.getBean(MediaPlayer.class);
组件扫描(component scanning)
自动装配(autowiring)@Autowired
用在构造器;
用在属性 Setter 方法;
用在(私有)属性;
required=false
Bean 的作用域
@Scope 可以与 @Component 和 @Bean 一起使用,指定作用域
Singleton,单例,不使用 @Scope 时默认,在整个应用中,只创建 bean 的一个实例Prototype,原型,每次注入或者通过 Spring 应用上下文获取的时候,都会创建一个新 bean 实例Session,会话,在 Web 应用中,为每个会话创建一个 bean 实例Request,请求,在 Web 应用中,为每个请求创建一个 bean 实例
使用会话和请求作用域:
1 2 3 4 5 @Component @Scope(value=WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_SESSION, proxyMode=ScopedProxyMode.INTERFACES) public ShoppingCart cart () {
面向切面编程
参见代码 section3。
AOP 术语
通知(Advice):切面做什么以及何时做
切点(Pointcut):何处
切面(Aspect):Advice 和 Pointcut 的结合
连接点(Join point):Spring 切面可以在方法前后连接,不可以在字段修改、构造方法上连接
引入(introduction):引入新的行为和状态
织入(Weaving):切面应用到目标对象的过程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 @Aspect public class Audience {@Before("execution(* concert.Performance.perform( .. ))") public void silenceCellPhones () {"Silencing cell phones" );@Before("execution(* concert.Performance.perform( .. ))") public void takeSeats () {"Taking seats" );@AfterReturning("execution(* concert.Performance.perform( .. ))") public void applause () {"CLAP CLAP CLAP!!!" );@AfterThrowing("execution(* concert.Performance.perform( .. ))") public void demandRefund () {"Demand a refund" );
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 @Aspect public class Audience1 {@Pointcut("execution(* concert.Performance.perform( .. ))") public void performance () {@Before("performance()") public void silenceCellPhones () {"Silencing cell phones" );@Before("performance()") public void takeSeats () {"Taking seats" );@AfterReturning("performance()") public void applause () {"CLAP CLAP CLAP!!!" );@AfterThrowing("performance()") public void demandRefund () {"Demand a refund" );
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 @Aspect public class Audience2 {@Pointcut("execution(* concert.Performance.perform( .. )) ") public void performance () {@Around("performance()") public void watchPerformance (ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {try {".Silencing cell phones" );".Taking seats" );".CLAP CLAP CLAP!!!" );catch (Throwable e) {".Demanding a refund" );
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Configuration @EnableAspectJAutoProxy public class ConcertConfig {@Bean public Performance concert () {return new Concert ();@Bean public EncoreableIntroducer encoreableIntroducer () {return new EncoreableIntroducer ();
@Controller、@Service 和 @Repository 三个注解本身有 @Component 的实例化效果。
AspectJ 切点指示器(pointcut designator)
例子:
1 2 3 4 5 @Pointcut( "execution(* soundsystem.CompactDisc.playTrack( int )) " + "&& args(trackNumber)")
另一个例子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Around("@annotation(innerAuth)") public Object innerAround (ProceedingJoinPoint point, InnerAuth innerAuth) {@InnerAuth public R<Boolean> register (@RequestBody SysUser sysUser) {
Web 开发框架
lombok
参考《Spring 实战(第 5 版)》2.1.1 节。
依赖:
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > org.projectlombok</groupId > <artifactId > lombok</artifactId > </dependency >
lombok 只在编译过程中起作用,编译期后就不需要了,要排除:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId > <configuration > <excludes > <exclude > <groupId > org.projectlombok</groupId > <artifactId > lombok</artifactId >
作用是简化代码书写,提供一些注解,帮助自动生成一些方法。
Spring MVC 的请求映射注解
参考《Spring 实战(第 5 版)》表 2.1。
@RequestMapping通用的请求处理,一般只在类级别使用
@GetMapping处理 HTTP GET 请求
@PostMapping处理 HTTP POST 请求
@PutMapping处理 HTTP PUT 请求
@DeleteMapping处理 HTTP DELETE 请求
@PatchMapping处理 HTTP PATCH 请求
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 @Slf4j @Controller @RequestMapping("/orders") @SessionAttributes("tacoOrder") public class OrderController {@GetMapping("/current") public String orderForm () {return "orderForm" ;@PostMapping public String processOrder (@Valid TacoOrder order, Errors errors, SessionStatus sessionStatus) {if (errors.hasErrors()) {return "orderForm" ;"Order submitted: {}" , order);return "redirect:/" ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 @Slf4j @Controller @RequestMapping("/design") @SessionAttributes("tacoOrder") public class DesignTacoController {@ModelAttribute public void addIngredientsToModel (Model model) {new Ingredient ("FLTO" , "Flour Tortilla" , Type.WRAP),new Ingredient ("COTO" , "Corn Tortilla" , Type.WRAP),new Ingredient ("GRBF" , "Ground Beef" , Type.PROTEIN),new Ingredient ("CARN" , "Carnitas" , Type.PROTEIN),new Ingredient ("TMTO" , "Diced Tomatoes" , Type.VEGGIES),new Ingredient ("LETC" , "Lettuce" , Type.VEGGIES),new Ingredient ("CHED" , "Cheddar" , Type.CHEESE),new Ingredient ("JACK" , "Monterrey Jack" , Type.CHEESE),new Ingredient ("SLSA" , "Salsa" , Type.SAUCE),new Ingredient ("SRCR" , "Sour Cream" , Type.SAUCE)for (Type type : types) {@ModelAttribute(name = "tacoOrder") public TacoOrder order () {return new TacoOrder ();@ModelAttribute(name = "taco") public Taco taco () {return new Taco ();@GetMapping public String showDesignForm () {return "design" ;@PostMapping public String processTaco ( @Valid Taco taco, Errors errors, @ModelAttribute TacoOrder tacoOrder) {if (errors.hasErrors()) {return "design" ;"Processing taco: {}" , taco);return "redirect:/orders/current" ;private Iterable<Ingredient> filterByType ( List<Ingredient> ingredients, Type type) {return ingredients
Spring Web 开发框架的分层【可能考简答】
graph LR
请求 --> 控制器层ProductsController --> 业务层ProductsService --> 数据访问层ProductsMapper --> 数据库
客户端请求参数分类
路径参数,@PathVariable
请求参数(查询参数),@RequestParam
表单参数,应用于前后端不分离的传统场景,默认,对应 model 对象,可以使用 @Valid 校验
json 请求体,应用于前后端分离的场景,使用 @RequestBody 把 json 格式转成 java 对象;@ResponseBody,把 java 对象转成 json 格式
处理流程
根据 url 找到控制器,控制器解析并获取参数,同时将转向业务层进行处理
涉及到数据的持久化则访问数据访问层,访问完毕后返回业务层,业务层处理完毕将结果数据返回到控制器
控制器处理分两种情况:
前后端分离:返回 Java 对象,同时加上 @ResponseBody 注解;客户端请求页面、json 格式数据,分别处理路径是什么?
前后端不分离:控制器将数据赋值给 model 的属性,同时返回视图名。根据视图名做视图解析,找到模板路径,通过第三方页面渲染,将 model 数据渲染到最终页面中,返回 html 格式文件。
在类的上方加注解 @RestController。
TODO:看第 13 次课,视频 1:36 处。
Spring Data JDBC、JPA【可能考简答】
重点分析三个例子的区别。
实现具体类
需要
不需要,只要写明继承关系
不需要,只要写明继承关系
定义实体类和数据库表的映射关系
不需要
需要
需要
程序员维护表之间的关系
需要
不需要
不需要
显式提供表结构(建表 SQL 脚本)
需要
需要
不需要,可以自动推断
使用 JdbcTemplate
参考代码 taco-cloud-jdbctemplate
特点:
解决 RawJdbcIngredientRepository 样板式代码的问题,只需要提供查询逻辑;
需要实现具体类 JdbcIngredientRepository 而其他两种方法不用;
需要提供 src/main/resources/schema.sql 文件作为表结构的定义(建表脚本)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > com.h2database</groupId > <artifactId > h2</artifactId > <scope > runtime</scope > </dependency >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @Repository public class JdbcIngredientRepository implements IngredientRepository {private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;public JdbcIngredientRepository (JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {this .jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;@Override public Iterable<Ingredient> findAll () {return jdbcTemplate.query("select id, name, type from Ingredient" ,this ::mapRowToIngredient);
使用 Spring Data JDBC
参考代码 taco-cloud-jdbc
特点:
需要定义实体类和数据库表的映射关系;
不需要实现具体类,只需要写好继承关系;
需要提供 src/main/resources/schema.sql 文件作为表结构的定义(建表脚本)。
1 2 3 4 public interface IngredientRepository extends CrudRepository <Ingredient, String> {
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;import org.springframework.data.relational.core.mapping.Table;@Data @Table @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE, force = true) public class Ingredient implements Persistable <String> {@Id private String id;private String name;private Type type;@Override public boolean isNew () {return true ;public enum Type {
使用 JDA
参考代码 taco-cloud-jpa
特点:
需要定义实体类和数据库表的映射关系;
不需要实现具体类,只需要写好继承关系;
依据实体类推断表结构,不需要建表脚本;
可以自定义查询方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public interface IngredientRepository extends CrudRepository <Ingredient, String> {
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 import javax.persistence.Entity;import javax.persistence.Id;@Data @Entity @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE, force = true) public class Ingredient {@Id private String id;private String name;private Type type;public enum Type {
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 @Data @Entity public class Taco {@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) private Long id;@NotNull @Size(min = 5, message = "Name must be at least 5 characters long") private String name;private Date createdAt = new Date ();@Size(min = 1, message = "You must choose at least 1 ingredient") @ManyToMany() private List<Ingredient> ingredients = new ArrayList <>();public void addIngredient (Ingredient ingredient) {this .ingredients.add(ingredient);
自定义的查询方法
定义查询方法,无需实现:
领域特定语言(domain specific language DSL)spring data 的命名约定
查询动词 + 主题 + 断言
查询动词: get 、 read 、 find 、 count
例子:
1 List<TacoOrder> findByDeliveryZip ( String deliveryZip ) ;
声明自定义查询(JDQL 面向对象查询语言):
不符合方法命名约定时,或者命名太长时
1 2 @Query("Order o where o.deliveryCity = 'Seattle'") readOrdersDeliveredInSeattle ( ) ;
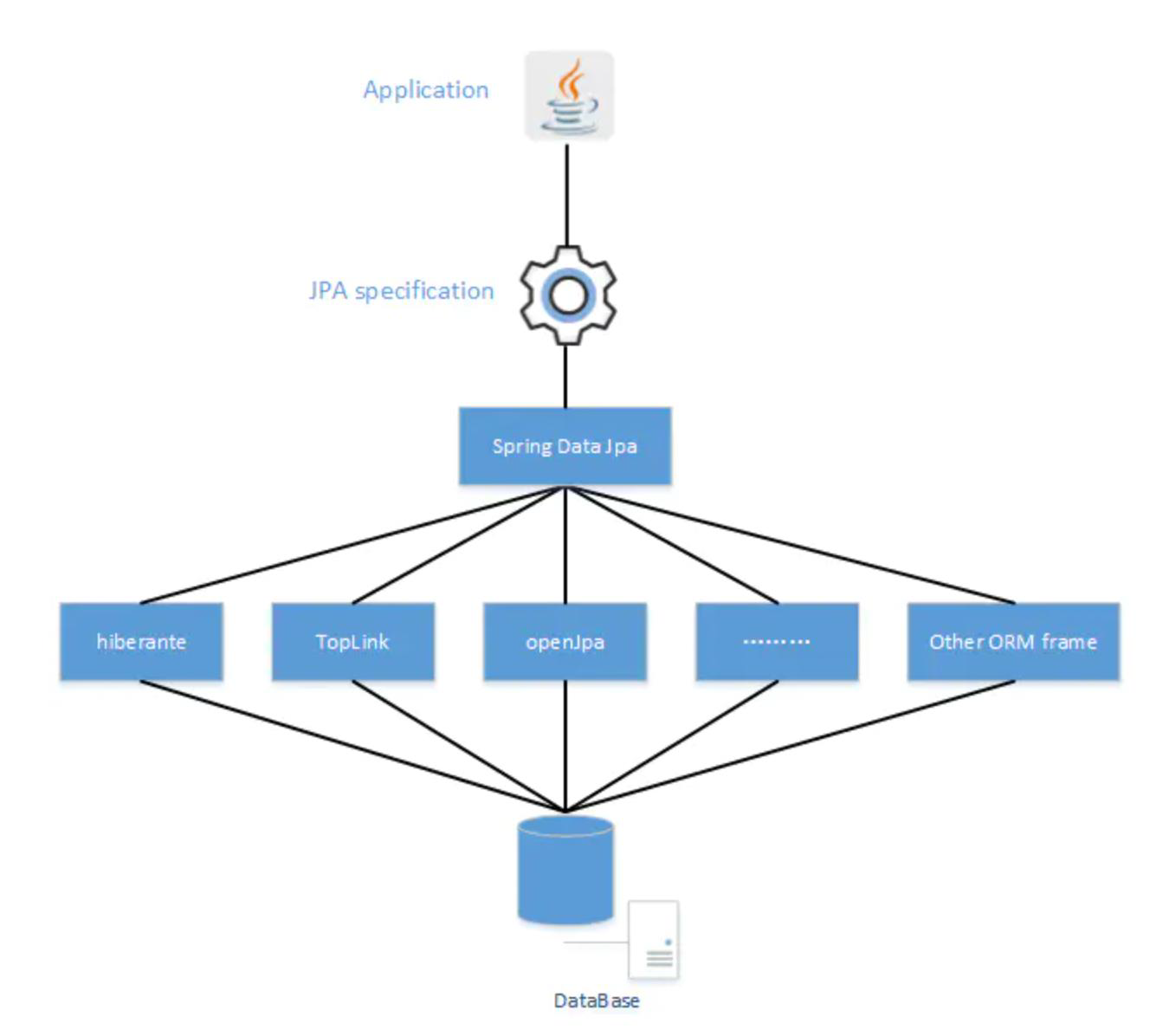
Jpa、Hibernate、Spring Data Jpa 三者之间的关系
JPA 的宗旨是为 POJO 提供持久化标准规范;
Hibernate 作为厂家实现了这一规范;
Spring Security
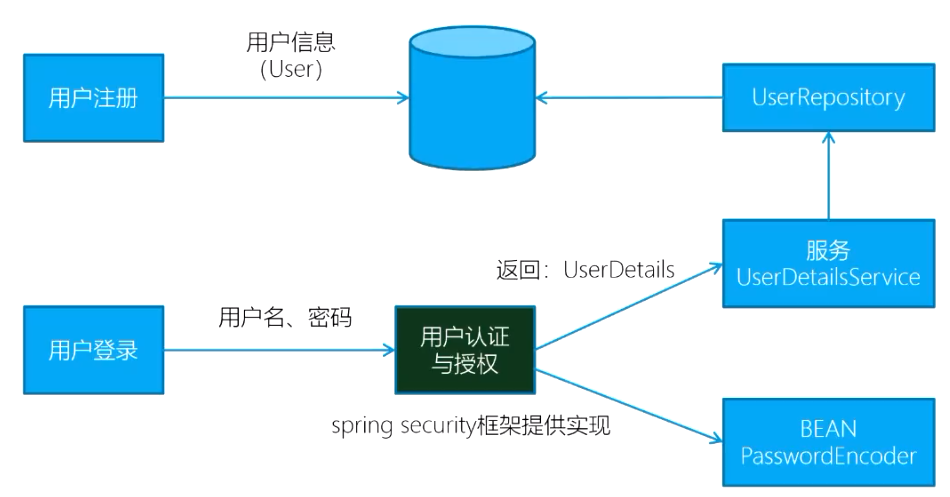
用户信息存储【可能考简答】
内存用户存储
JDBC 用户存储
LDAP(Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) 用户存储
保护请求
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 @Override protected void configure (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {"/design" , "/orders" ).access("hasRole('USER')" )"/" , "/**" ).access("permitAll" )"/login" )"/" )"/h2-console/**" )
创建自定义登录页
当需要认证时转向的登录页:.loginPage("/")
视图控制器,定义 login 请求对应的视图:registry.addViewController("/login");
登录的 post 请求由 Spring Security 自动处理,名称默认:username、password,可配置
总结
Docker 使用
Docker 10 分钟快速入门_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
docker run 命令
-d:后台运行容器,并返回容器 ID-i:以交互模式运行容器,通常与 -t 同时使用-t:为容器重新分配一个伪输入终端,通常与 -i 同时使用-p:指定(发布)端口映射,格式为:主机(宿主)端口:容器端口-P:随机端口映射,容器内部端口随机映射到主机的高端口--name="nginx lb":为容器指定一个名称-e username="ritchie":设置环境变量--env-file=c:/temp1/t1.txt:从指定文件读入环境变量--expose=2000-2002:开放(暴露)一个端口或一组端口;--link my-mysql:taozs:添加链接到另一个容器-v c:/temp1:/data:绑定一个卷(volume)--rm :退出时自动删除容器
其他命令
查看容器 IP 地址:cat /etc/hosts
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 > docker --help
容器镜像构建与编排
Dockerfile 文件的指令
参考《Spring 微服务实战(第 2 版)》表 4-1。
FROM :指定基础镜像,必须为第一个命令RUN :构建镜像时执行的命令ADD :将本地文件添加到容器中 tar 类型文件会自动解压COPY :功能类似 ADD ,但是不会自动解压文件CMD :构建容器后调用,也就是在容器启动时才进行调用ENTRYPOINT :配置容器,使其可执行化。配合 CMD 可省去“application”,只使用参数,用于 docker run 时根据不同参数执行不同功能LABEL :用于为镜像添加元数据ENV :设置环境变量EXPOSE :指定与外界交互的端口,容器内的端口号 docker run 时加 P 则会映射一个随机号(宿主机)VOLUME :用于指定持久化目录 docker run 时如果没有指定挂载目录,会创建一个 volumeWORKDIR :工作目录,类似于 cd 命令USER :指定 运行容器时的用户名或 UIDARG :用于指定传递给构建运行时的变量ONBUILD :用于设置镜像触发器
Docker build
1 docker build [OPTIONS] PATH | URL | -
如何编写最佳的 Dockerfile:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/26904830
服务编排工具 docker-compose
Compose 项目是 Docker 官方的开源项目,负责实现对 Docker 容器集群的快速编排
一个单独的 docker-compose.yml 模板文件(YAML 格式)来定义一组相关联的应用容器为一个项目(project)
Compose 的默认管理对象是项目,通过子命令对项目中的一组容器进行便捷地生命周期管理
Compose 中有两个重要的概念:
服务(service):一个应用的容器(可能会有多个容器),实际上可以包括若干运行相同镜像的容器实例
项目(project):由一组关联的应用容器组成的一个完整业务单元,在 docker.compose.yml 文件中定义
使用微服务架构的系统一般包含若干个微服务,每个微服务一般部署多个实例。如果每个服务都要手动启停,那么效率低,维护量大
YAML 文件
使用缩进表示层级关系,不允许使用 Tab 键,只允许使用空格
# 表示注释,从这个字符一直到行尾,都会被解析器忽略。对象,键值对,使用冒号结构表示:
1 2 animal: pets hash: { name: Steve , foo: bar }
数组,一组连词线开头的行,构成一个数组
docker-compose 常用命令
参考《Spring 微服务实战(第 2 版)》表 4-3。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 docker-compose --help
k8s 使用
[K8S] 什么是 Kubernetes?8 岁小孩能看懂的版本_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
从第 14 次视频 1:43:21 开始。
k8s 中的资源
namespaces
Pods
ReplicaSet
Deployment
Service
Ingress
configmap
secrets
serviceaccounts
DaemonSetf
Pod
Pod 是 Kubernetes 调度的最小单元。
一个 Pod 可以包含一个或多个容器,因此它可以被看作是内部容器的逻辑宿主机。Pod 的设计理念是为了支持多个容器在一个 Pod 中共享网络和文件系统。
Volumes:Pod 中各个容器可以共享在 Pod 中定义分存储卷(Volume),就像是 Pod 自己的文件系统。
PID 命名空间:Pod 中不同的应用程序可以看到其他应用程序的进程 ID
network 命名空间:Pod 中多个容器处于同一个网络命名空间,因此能够访问的 IP 和端口范围都是相同的。也可以通过 localhost 相互访问
IPC 命名空间:Pod 中的多个容器共享 Inner-process Communication 命名空间,因此可以通过 SystemV IPC 或 POSIX 进行进程间通信
UTS 命名空间:Pod 中的多个容器共享同一个主机名
访问服务的三种方法
将 pod 或 service 的端口快速映射到本机端口(调试时访问端口用)
1 2 kubectl port-forward pod/myspittr 8081:8080 # 访问: http://localhost:8081/spittr/
创建 ingress
Ingress 是 Kubernetes 中的一种 API 对象类型,它允许将 HTTP 和 HTTPS 流量路由到 Kubernetes 集群内的不同服务。
简单来说,Ingress 是一种在 Kubernetes 上实现负载均衡、路由和 HTTPS 终止的方法。
1 2 kubectl create ingress myspittr --class=nginx --rule=www.demo.com/*=myspittr:8080 # 访问: http://www.demo.com/spittr/
通过 curl 工具来访问 k8s 服务
1 kubectl run -i -t --rm=true mycurl --image=curlimages/curl:latest --restart=Never --command --sh # 不在幻灯片上,但是强调过
Label、service 和 pod 之间的关系
Deployment
自动伸缩,设定伸缩个数的区间:
1 kubectl autoscale deployment spittr --min=10 --max=15 --cpu-percent=80
k8s 和 nacos 服务的异同点【可能考简答】
从第 14 次视频 1:49:50 开始。
共同点:
通过服务名访问多个服务;
一个服务背后可能有多个服务实例;
通过 Pod 来体现;
服务实例是动态的,客户只需要知道服务名即可
不同点:
k8s 服务是 pod 层级的;nacos 服务是服务层级的,和开发框架相关;
nacos 的服务启动、升级、重启需要依赖底层 k8s(课上录屏内容);
k8s 和 nacos 都可以完成服务注册与发现,但 k8s 部署门槛和资源消耗 更大。
REST 服务、微服务开发与部署
从第 14 次视频 1:59:16 开始。
微服务架构模式的特征【可能考简答】
参考《Spring 微服务实战(第 2 版)》1.1.3 节。
应用程序分解为具有明确定义了职责范围的细粒度组件
完全独立部署,独立测试,并可复用
使用轻量级通信协议 HTTP 和 JSON ,松耦合
服务实现可使用多种编程语言和技术
将大型团队划分成多个小型开发团队,每个团队只负责他们各自的服务
响应头与响应体
状态行:由 HTTP 协议版本、状态码、状态码描述三部分构成,它们之间由空格隔开。
状态码 :由 3 位数字组成,第一位标识响应的类型,常用的 5 大类状态码如下:
1xx :表示服务器已接收了客户端的请求,客户端可以继续发送请求
2xx :表示服务器已成功接收到请求并进行处理
3xx :表示服务器要求客户端重定向
4xx :表示客户端的请求有非法内容
5xx :标识服务器未能正常处理客户端的请求而出现意外错误
响应头:
Location :服务器返回给客户端,用于重定向到新的位置
Server 包含服务器用来处理请求的软件信息及版本信息 Vary :标识不可缓存的请求头列表
Connection: 连接方式, close 是告诉服务端,断开连接,不用等待后续的请求了。 keep alive 则是告诉服务端,在完成本次请求的响应后,保持连接
Keep Alive: 300 ,期望服务端保持连接多长时间(秒)
响应内容:服务端返回给请求端的文本信息。
消息转换器 Message conversion
使用方法级注解 @ResponseBody 或类级 @RestController 作用:指定使用消息转换器,把 Java 对象转化成 json 文件 没有 model 和视图,控制器产生数据,然后消息转换器转换数据之后的资源表述。
spring 自动注册一些消息转换器(HttpMethodConverter),不过类路径下要有对应转换能力的库,如:Jackson Json processor、JAXB 库
请求传入,方法级注解 @RequestBody 以及 HttpMethodConverter,把来自客户端的 json 数据转化成 java 对象 。
示例代码
1 2 3 @SpringBootApplication @Configuration @ComponentScan
健康检查: 加了 actuator 后可以获得更多端点,如 health。
运维实践【可能考简答】
功能代码和测试脚本等都在源代码库中
指定 JAR 依赖的版本号
配置数据与源代码分开放,配置当中有很多常变化的、敏感的信息
已构建的服务是不可变的,不能再被修改
微服务应该是无状态的
并发,通过启动更多的微服务实例横向扩展,多线程是纵向扩展
基于 NACOS 的数据配置
从第 14 次视频 2:04:17 开始。
配置
pom 配置
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > com.alibaba.cloud</groupId > <artifactId > spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config</artifactId > </dependency >
yml 配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 spring: application: name: licensingservice profiles: active: default cloud: nacos: config: server-addr: nacos-headless:8848 file-extension: yml
代码注解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @Component @RefreshScope public class ServiceConfig {@Value("${example.property}") private String exampleProperty;public String getExampleProperty () {return exampleProperty;
dataId 的完整格式
${prefix}-${spring.profiles.active}.${file-extension}
prefix 默认为 spring.application.name 的值,也可以通过配置项 spring.cloud.nacos.config.prefix 来配置 spring.profiles.active 即为当前环境对应的 profile。file-exetension 为配置内容的数据格式,可以通过配置项 spring.cloud.nacos.config.file-extension 来配置。 目前只支持 properties 和 yaml 类型。
基于 NACOS 的服务注册与发现
从第 14 次视频 2:10:16 开始。
使用 pod 测试
[9.3.3 通过 curl 工具来访问 k8s 服务](#通过 curl 工具来访问 k8s 服务) 中提到的代码:
1 2 3 kubectl run -i -t --rm=true mycurl --image=curlimages/curl:latest --restart=Never --command --sh
以上命令中 nacos-headless 处可以指定服务名,可以指定服务集群 IP,可以指定 pod IP,不可以指定 pod 名。
服务发现的好处【可能考简答】
快速水平伸缩(增减服务实例),而不是垂直伸缩(增减服务的线程)。不影响客户端
提高应用程序的弹性:容错性更强
Spring Cloud Alibaba
使用到的 starter 依赖
服务配置: com.alibaba.cloud, spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config
服务注册: com.alibaba.cloud, spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery
客户端负载均衡: org.springframework.cloud, spring-cloud-starter-loadbalancer
简化客户端调用: org.springframework.cloud, spring-cloud-starter-openfeign
调用服务的三种方式【可能考简答】
Spring DiscoveryClient
使用支持 LoadBalanced 的 RestTemplate
使用 OpenFeign (@FeignClient):OpenFeign 是一款声明式、模板化的 HTTP 客户端, Feign 可以帮助我们更快捷、优雅地调用 HTTP API
后两种方法自动做负载均衡,因此一般不建议使用第一种(只在测试时使用),更常见的是第三种。我们定义的负载平衡策略(轮询、随机等)能影响到后两种方式。
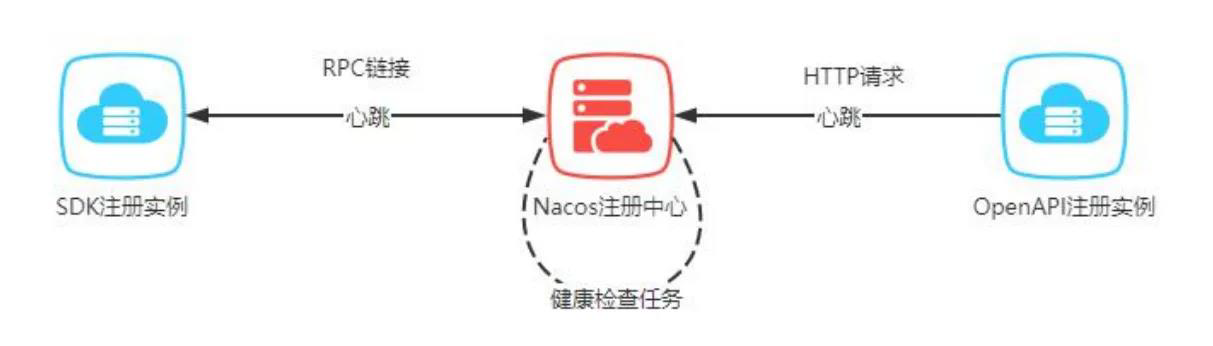
健康检查【可能考简答】
服务部署
由 A(licensingservice) 到 B(organizationservice) ,需要获得 B 的 IP 地址和端口号。
不是 A 先把请求发给 Nacos,由 Nacos 进行转发;
而是从 Nacos 获得 IP 地址,再直接和 B 进行通信。
如何基于 NACOS 实现服务注册与发现【可能考简答】
从第 14 次视频 2:15:46 开始。
分为以下三大步。
添加依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 <dependency > <groupId > com.alibaba.cloud</groupId > <artifactId > spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.cloud</groupId > <artifactId > spring-cloud-starter-loadbalancer</artifactId > </dependency >
定义访问地址
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 server: port: 8080 spring: application: name: licensingservice profiles: active: default cloud: nacos: config: server-addr: nacos-headless:8848 file-extension: yml discovery: server-addr: nacos-headless:8848
启动类注解
在 12.5 调用服务的三种方式【可能考简答】 中,只需要知道最常用的第三种方式即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 @SpringBootApplication @EnableDiscoveryClient @EnableFeignClients public class Application {public static void main (String[] args) {@LoadBalanced @Bean public RestTemplate getRestTemplate () {return new RestTemplate ();
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @FeignClient("organizationservice") public interface OrganizationFeignClient { @RequestMapping( method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "/v1/organizations/{organizationId}", consumes = "application/json") getOrganization (@PathVariable("organizationId") String organizationId) ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 @Service public class LicenseService {@Autowired @Autowired @Autowired @Autowired @Autowired private LicenseRepository licenseRepository;
基于 Sentinel 的流控与熔断
从第 14 次视频 2:20:30 开始。
Sentinel 是面向分布式、多语言异构化服务架构的流量治理组件,主要以流量为切入点,从流量路由、流量控制、流量整形、熔断降级、系统自适应过载保护、热点流量防护等多个维度来帮助开发者保障微服务的稳定性。
Sentinel 组成
核心库(Java 客户端):不依赖任何框架/库,能够运行于 Java 8 及以上的版本的运行时环境,同时对 Dubbo/Spring Cloud 等框架也有较好的支持
控制台(Dashboard Dashboard):主要负责管理推送规则、监控、管理机器信息等
控制台不维护规则,通过端口号 8719 查询规则,如果服务故障则规则丢失。
定义资源的方式
代码直接定义
使用注解定义
Spring Cloud 针对 URL 自动定义
强调:外置文件只能用来定义规则,不能用来定义资源
规则的种类【可能考简答】
流量控制规则
熔断降级规则
系统保护规则
来源访问控制规则
热点参数规则
熔断策略
慢调用比例
异常比例
异常数绝对值