In computing, a memory model describes the interactions of threads through memory and their shared use of the data.
Sequential Consistency (SC) Model [Lamport 1979]
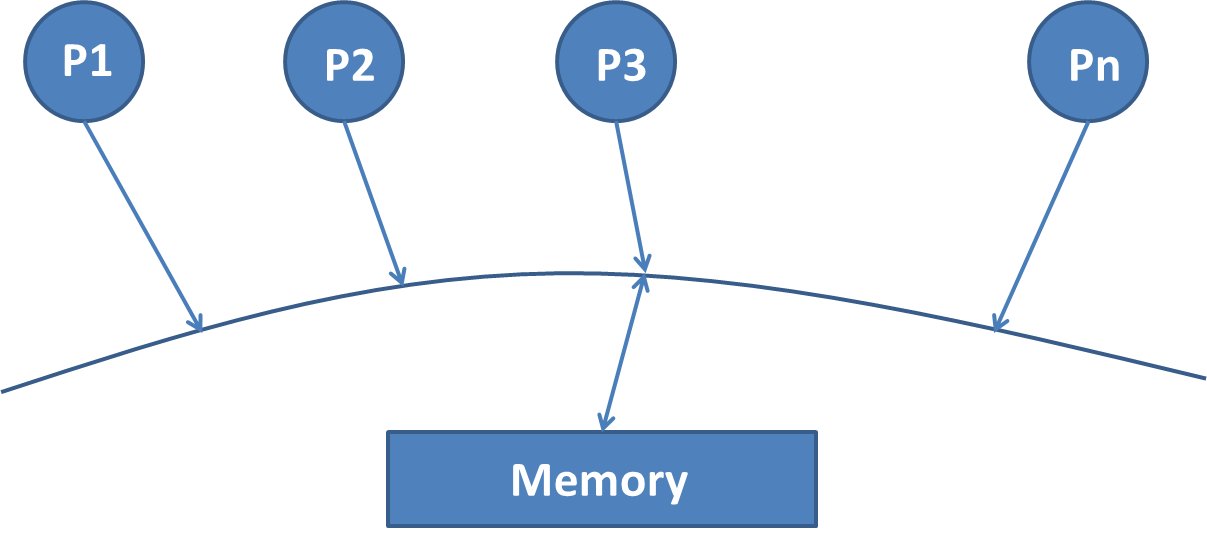
- No muticore processor implements SC
- Compiler optimizations invalidate SC
Weak/Relaxed Memory Models
Every hardware architecture has its own WMM
- x86-TSO memory model
- ARMv8 memory model
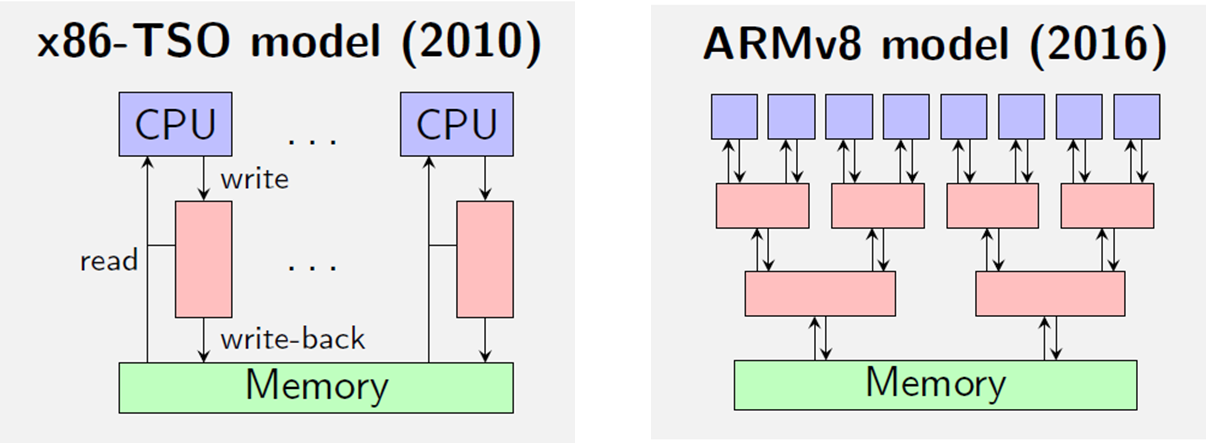
More than just reorderings [FM'16]
SC model prohibits many optimizations
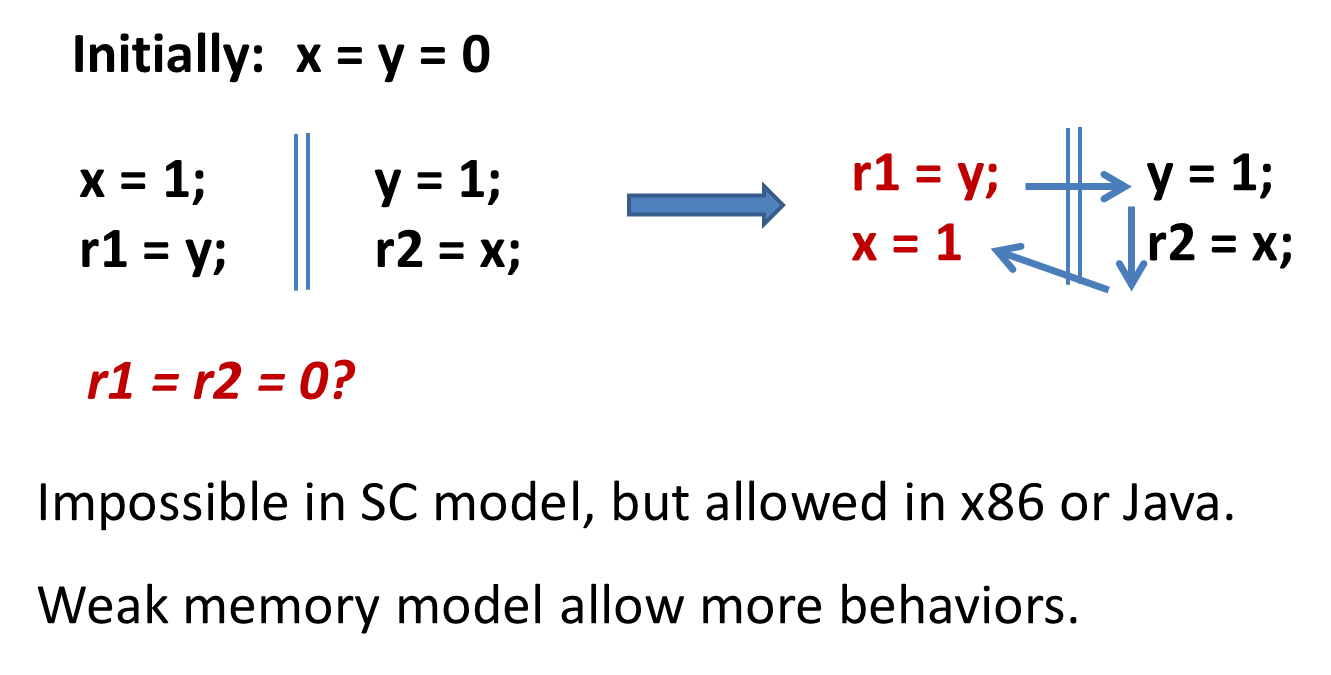
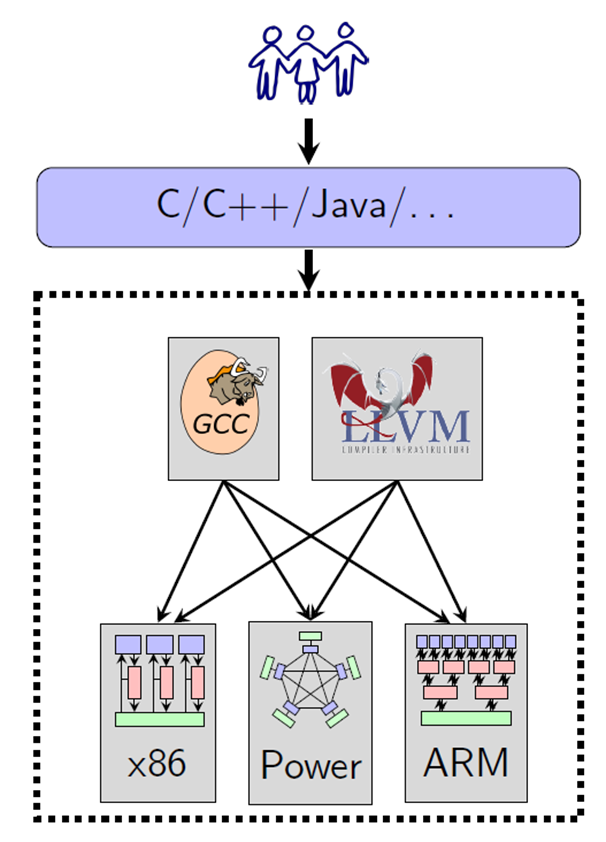
WMM for High-Level Languages
Design Criteria
Usability: DRF guarantee
- DRF programs have the same behaviors as in SC model
Not too strong:
- Allow common optimization techniques
- Allow standard compilation schemes to major modern architectures
- In some sense hijacked by the mainstream compiler
Preserve type-safety and security guarantee
- Cannot be too weak
Very challenging to satisfy all the requirements!
Data-Race-Freedom (DRF)
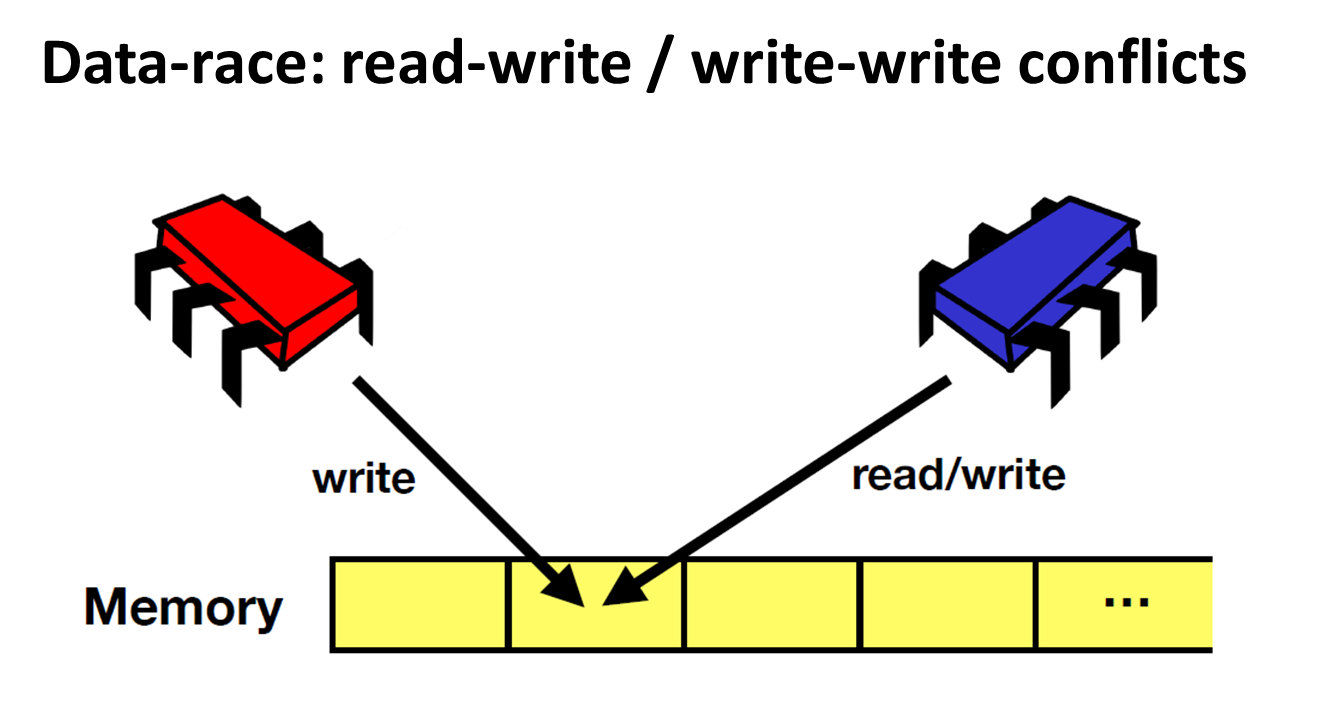
A data race occurs when we have two concurrent conflicting operations
- Conflicting: the two operations both access the same memory location and at least one is a write
- Concurrent ?
- Differs across memory models
- Java: the two operations are not ordered by “happens-before”
DRF Guarantee
DRF programs have the same behaviors as in SC model
For DRF programs, the programmer does not need to worry that reorderings will affect her code.
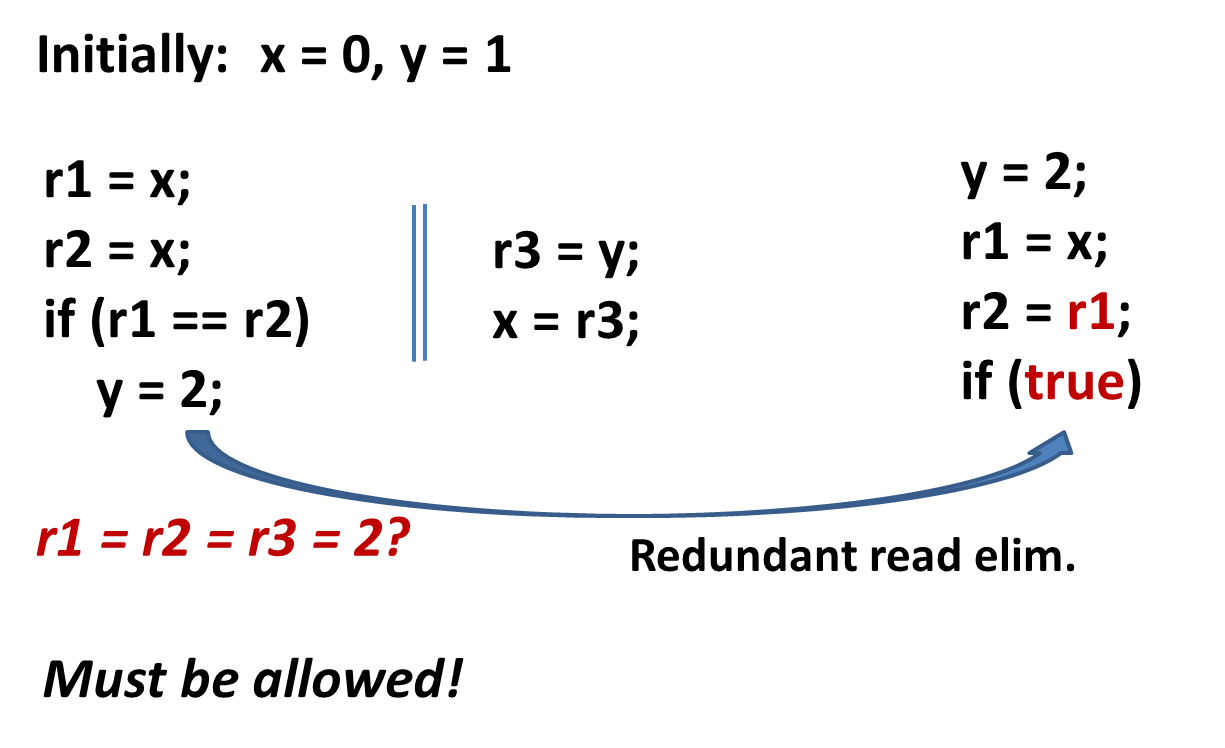
Compiler Optimization Can Be Smart
Efforts for Java Memory Model (JMM)
- First edition in Java Language Spec
- Fatally flawed, not support key optimizations [Pough 2000]
- Current JMM [Manson et al. 2005]
- Based on 5-year discussion and many failed proposals
- “very complex” [Adve & Boehm 2010]
- Surprising behaviors and bugs [Aspinall & Sevcik 2007]
- Next generation: JEP 188, Dec. 2013
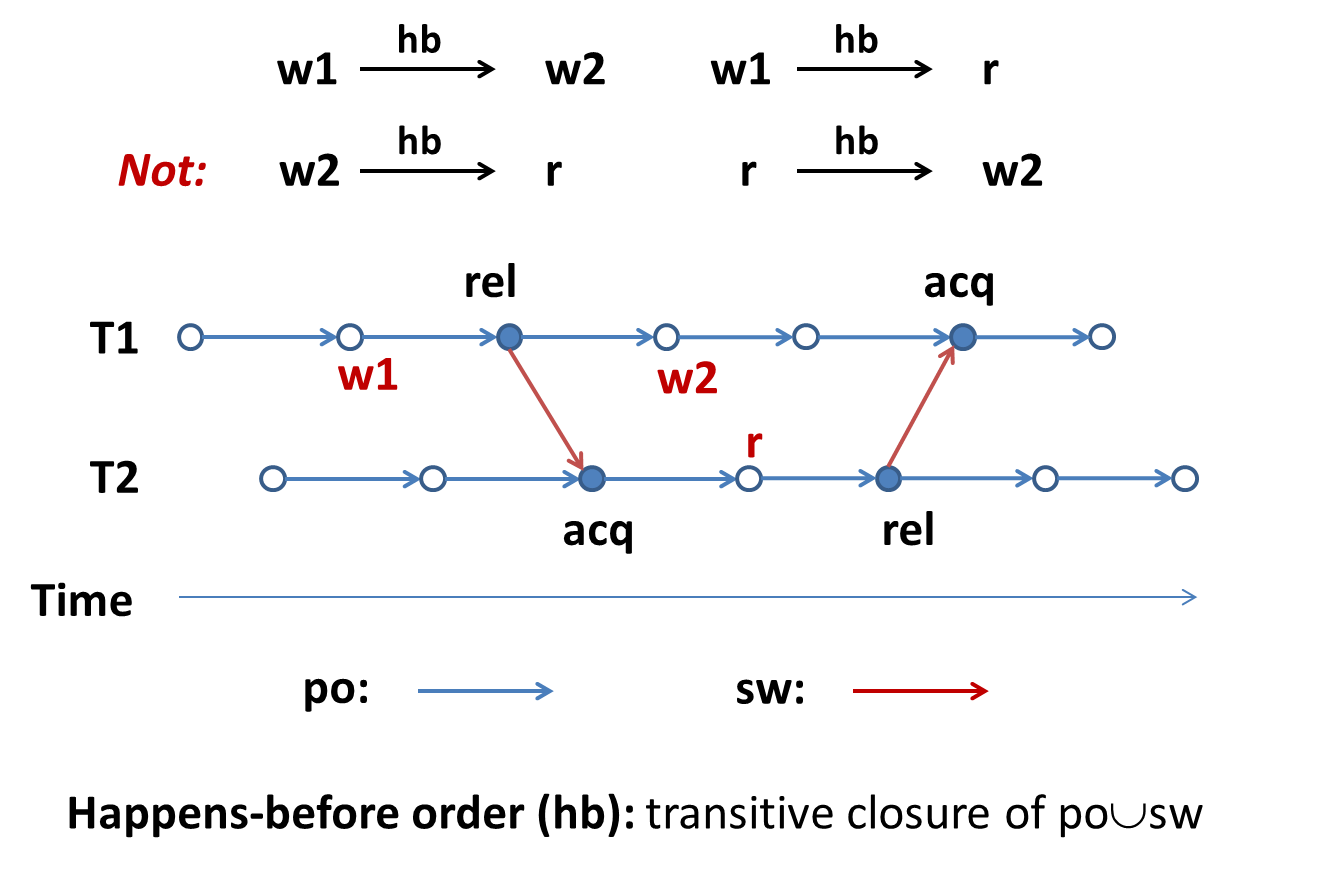
Happens-Before Order [Lamport 1978]
Program execution: a set of events, and some orders between them.
Happens-Before Memory Model (HMM)
Read can see:
- the most recent write that happens-before it, or
- a write that has no happens-before relation.
r could see both w1 (which happens-before it) and w2 (with which there is no happens-before relation)
HMM – Relaxed Ordering

HMM – Examples with Global Analysis
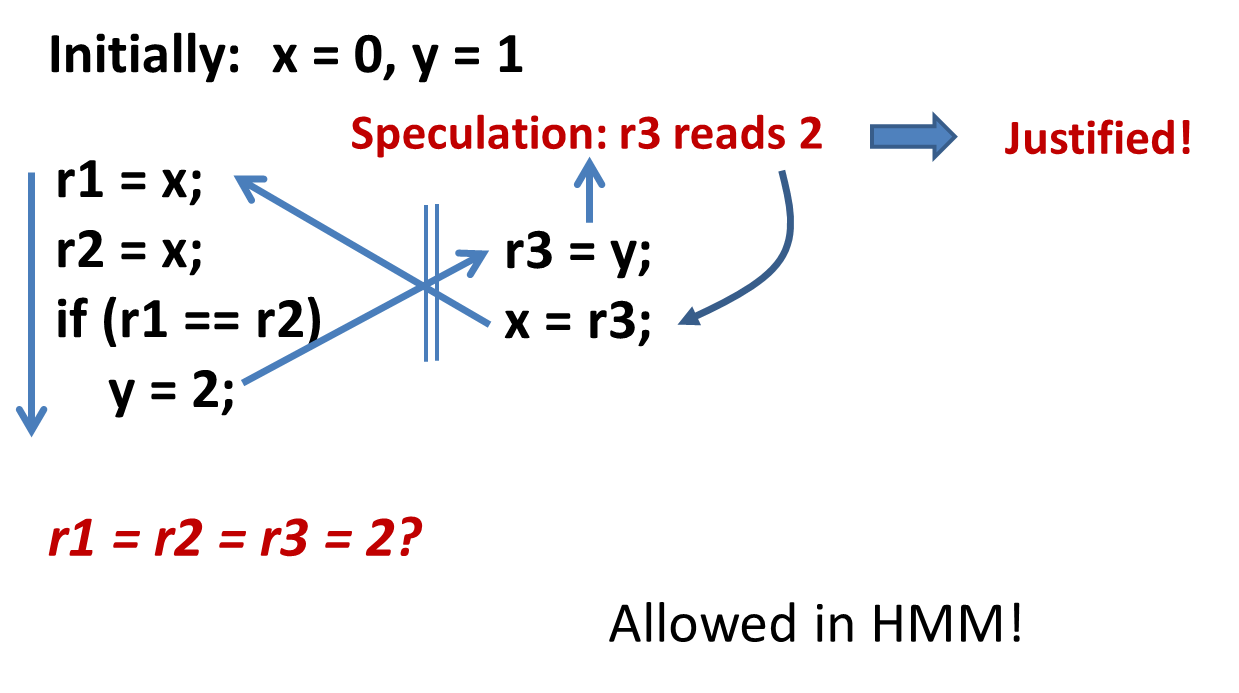
HMM – Out-of-Thin-Air Read
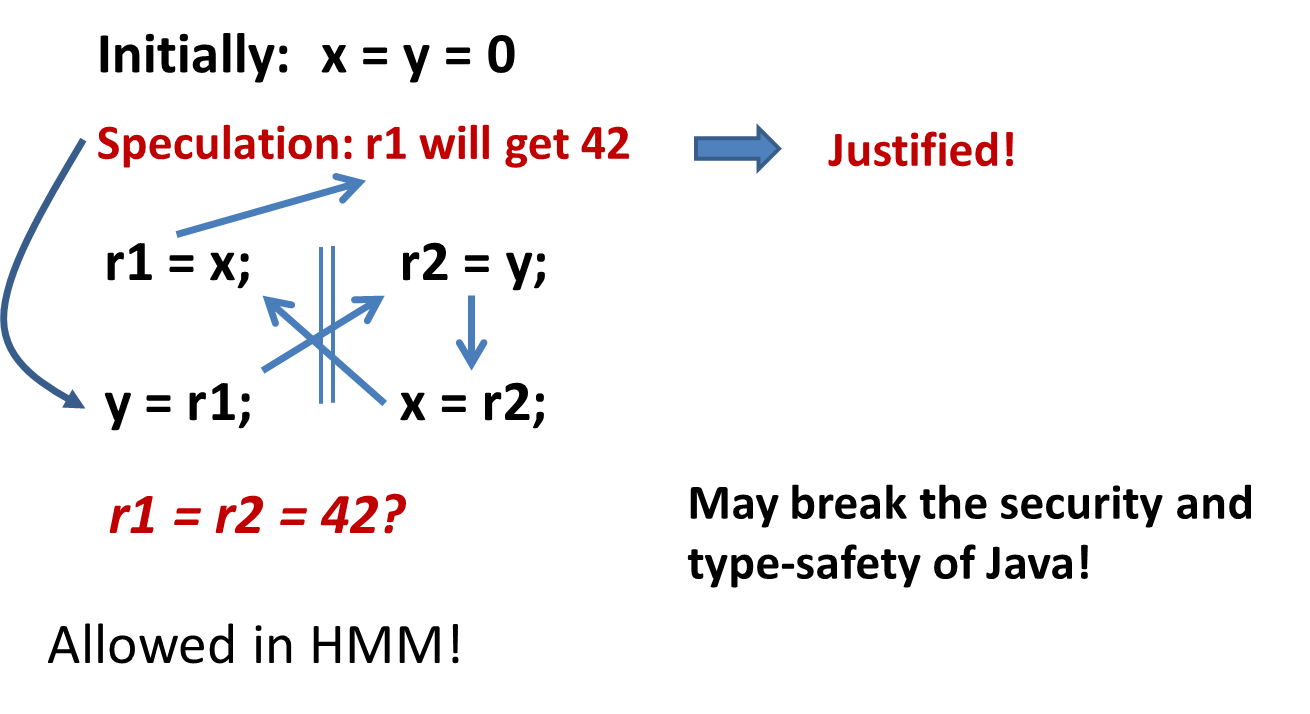
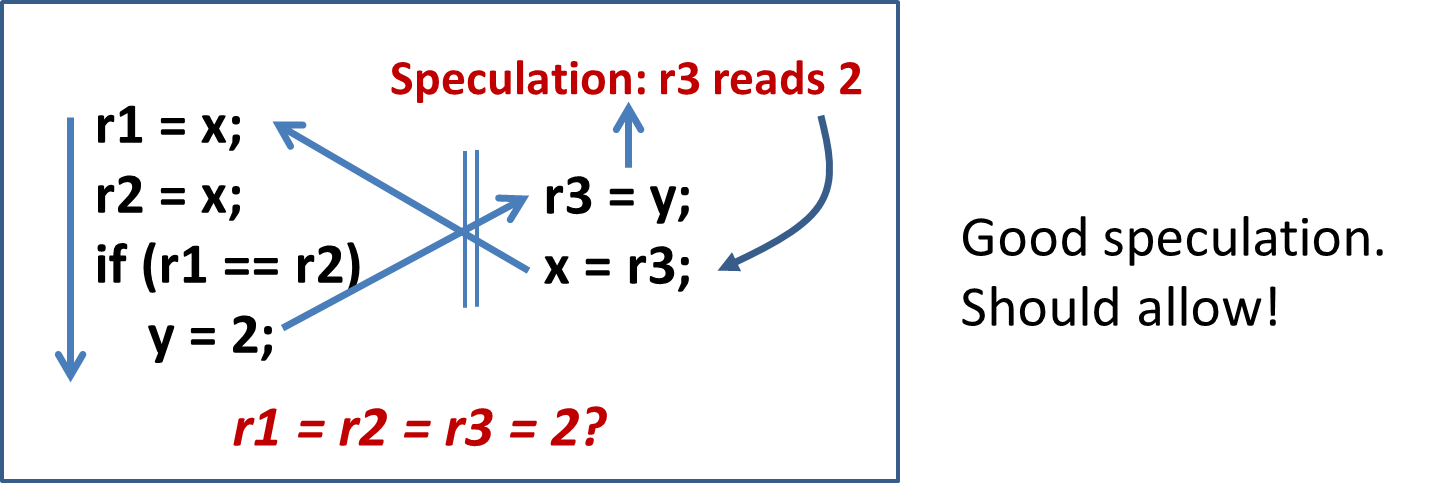

TODO:这几个例子看不明白
JMM
Take HMM as the core, and try hard to distinguish good speculation from bad speculation!
Introduce 9 axioms to constrain causality.
Very complex, with surprising results and bugs.
JMM – Surprising Results
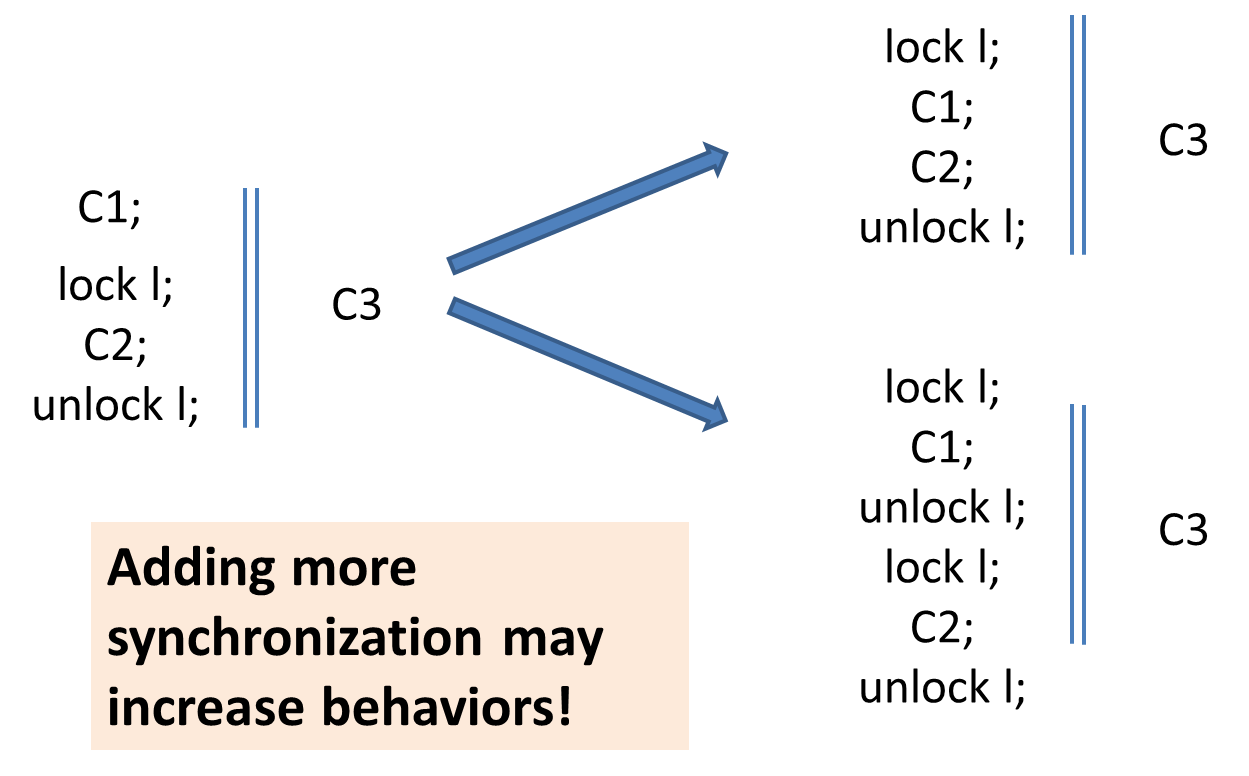
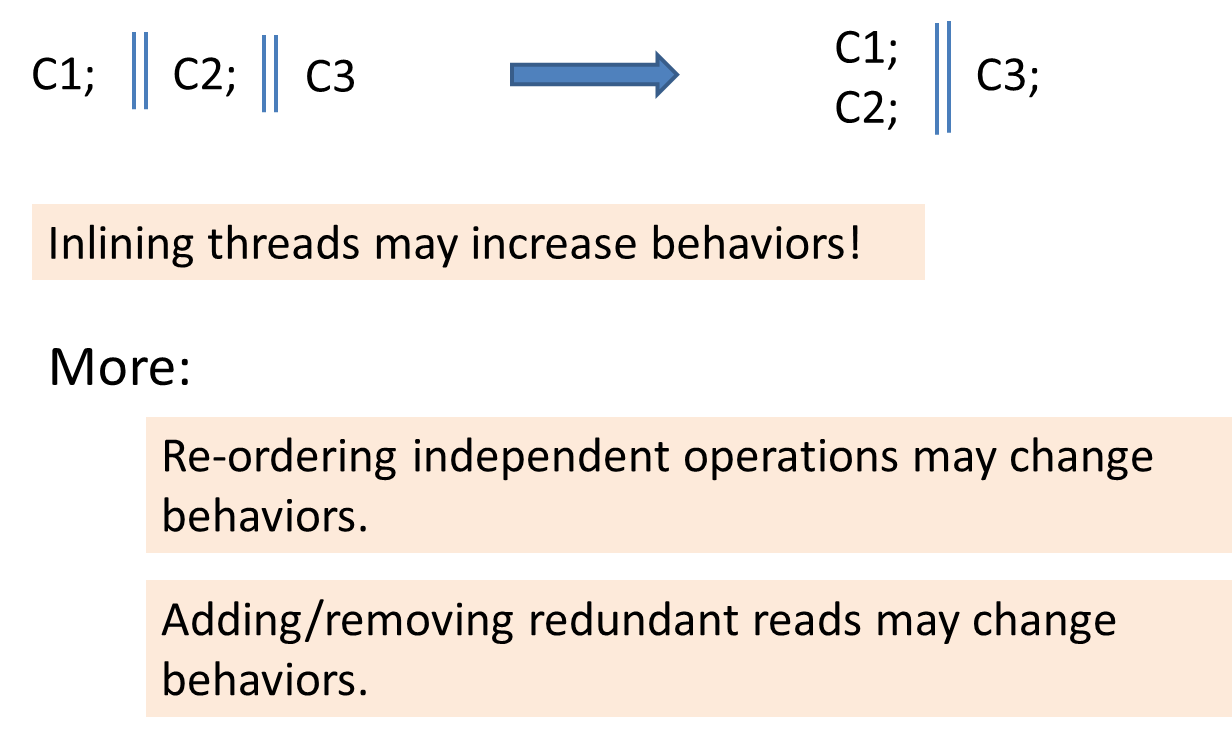
More Examples
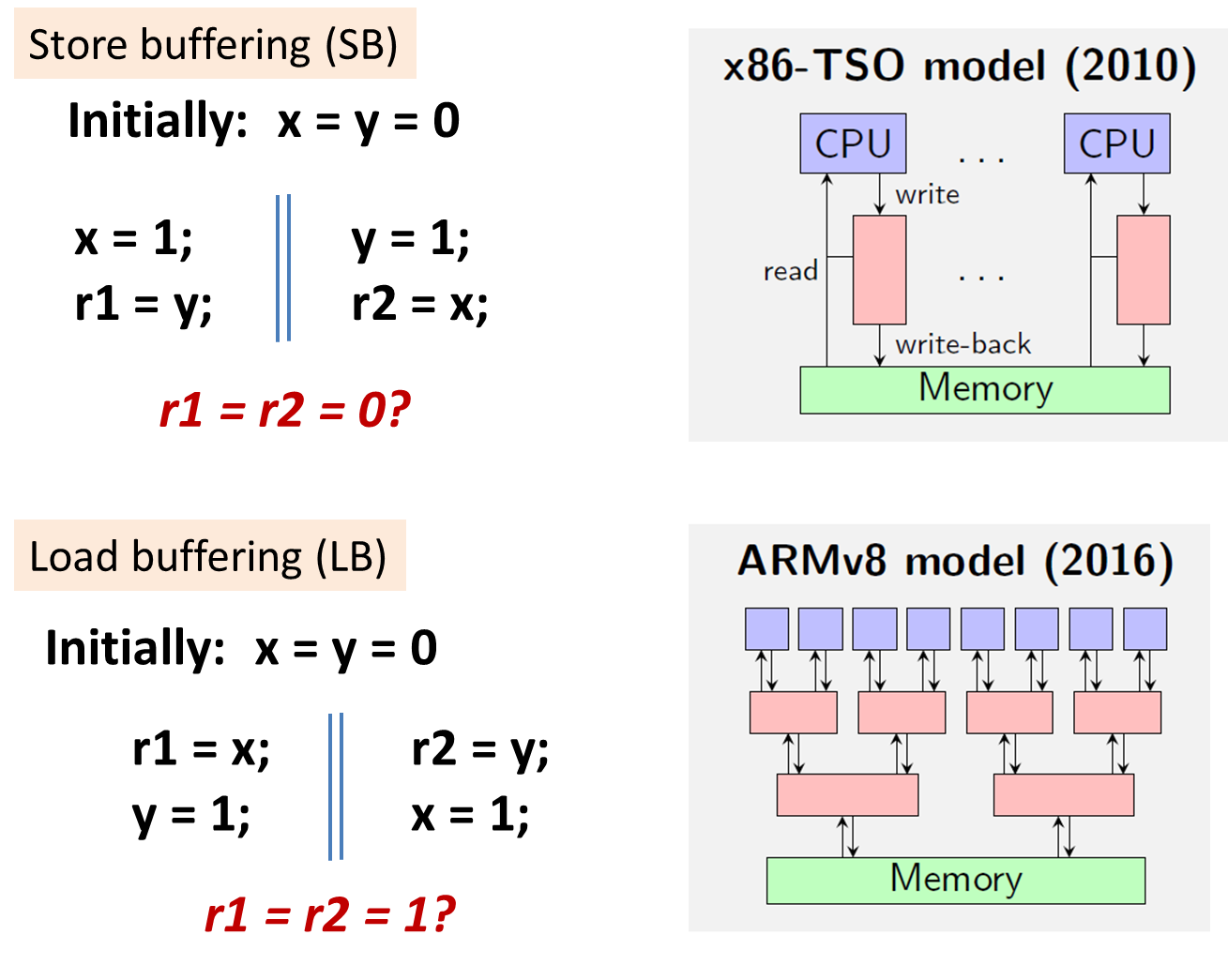
Load buffering (LB)
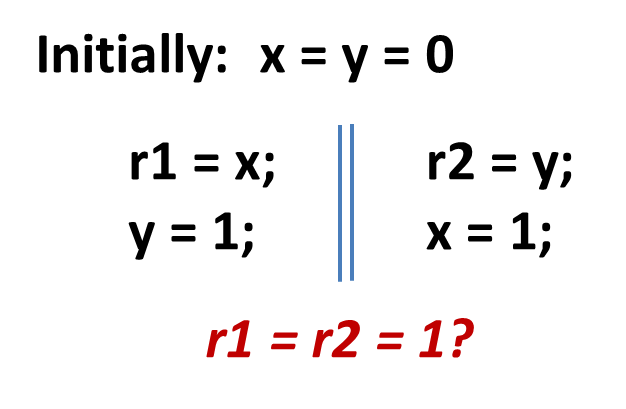
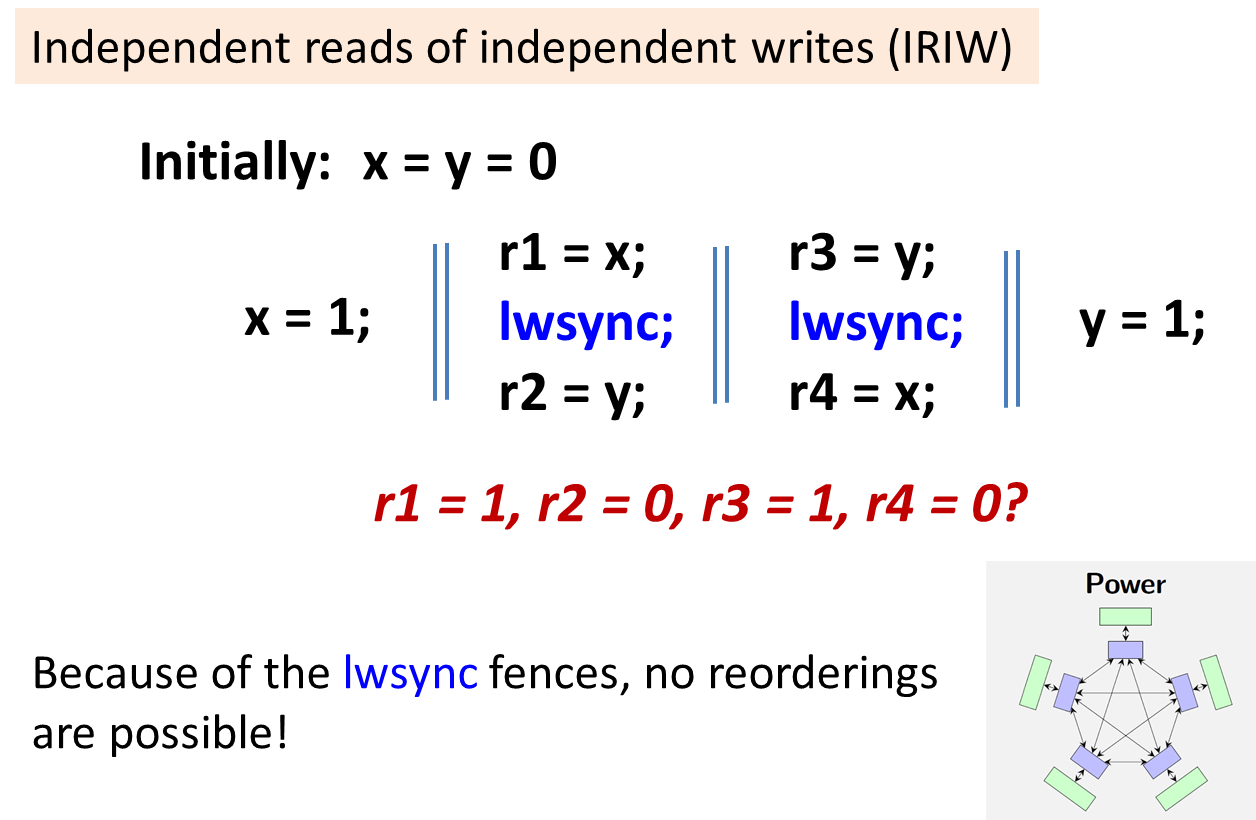
Independent reads of independent writes (IRIW)
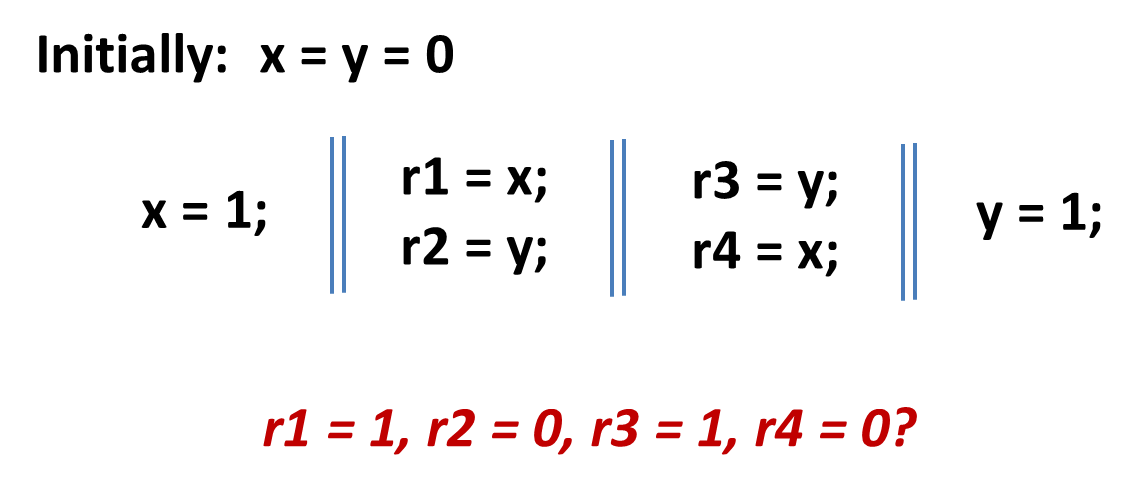
Out-of-thin-air read

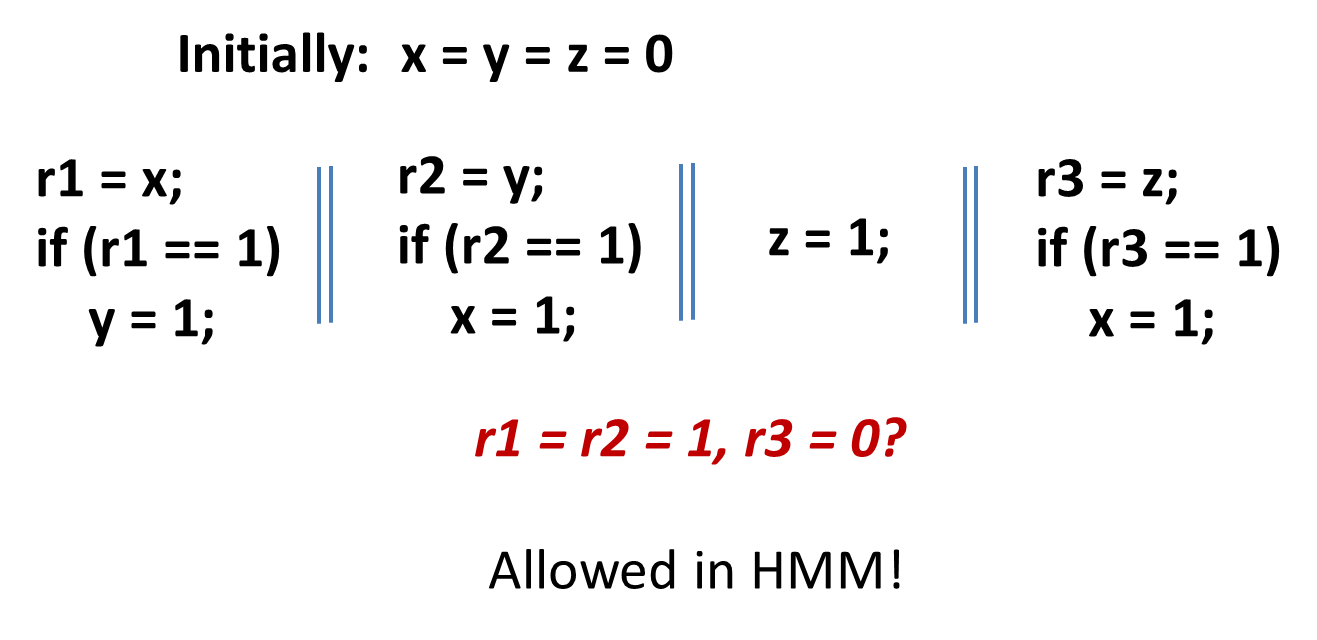
HMM does not have DRF-guarantee
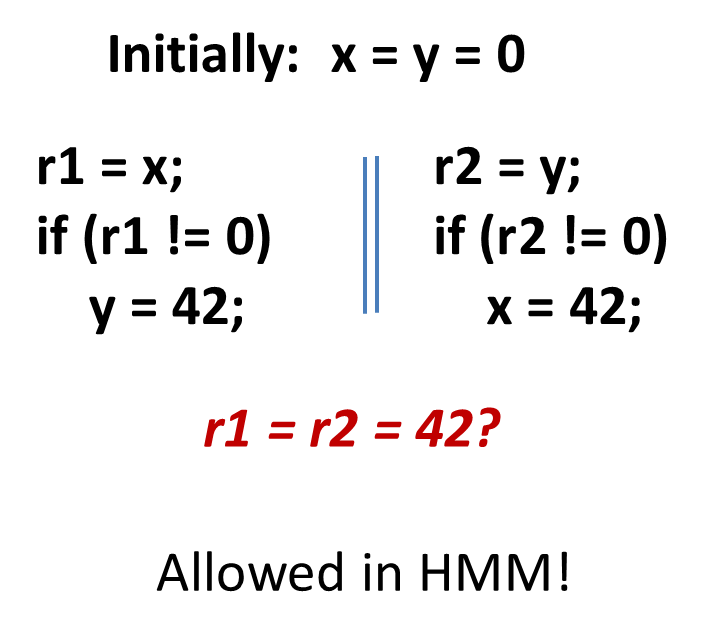
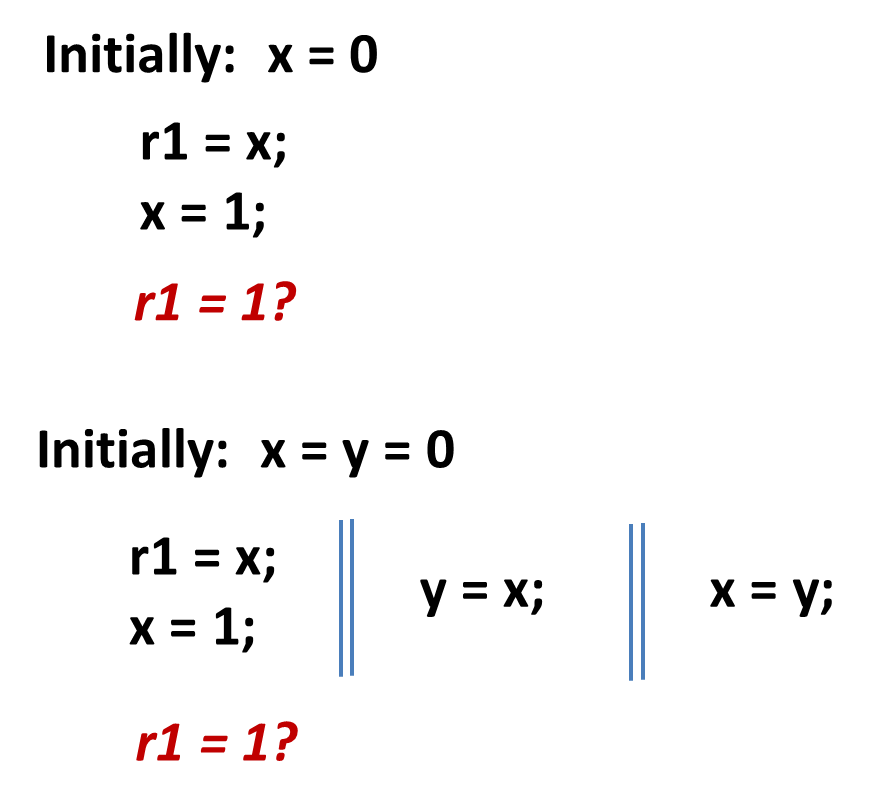
Summary
- Why need weak memory models
- Design criteria of weak memory models
- The happens-before memory model
- Out-of-thin-air read

